In general marketing terms, customer perception refers to customers’ awareness, their impressions, and their opinions about a business and its brand, along with its products and services. Customer perception can be shaped by both direct and indirect interactions with a brand’s offerings — it’s not entirely dependent upon marketing or upon the inherent quality of the product or service itself.
It may seem difficult, then, to control customer perception. While control might not actually be possible, there are several ways to influence how customers view companies through brand market research.
Customer behavior and perception of brands is not in all actuality driven by logic — from negative brand associations, to positive or even sentimental brand attachments. According to Harvard professor Gerald Zaltman, 95% of purchase decisions are subconscious. Remember that commercial jingle for an iconic software brand you grew up hearing on TV? It probably left a lasting impression on your young mind, and in turn given you a brand perception that is hard to let go of.
The intangible concept of customer perception is often at odds with the tangible effect on business outcomes, as customer perceptions of a company’s products or services can have a serious impact on the long term viability of a business’s offerings. Just ask any insights professional at Disney, a company that takes the motto “make people happy” very seriously by listening to the voice of the customer to improve its offerings.
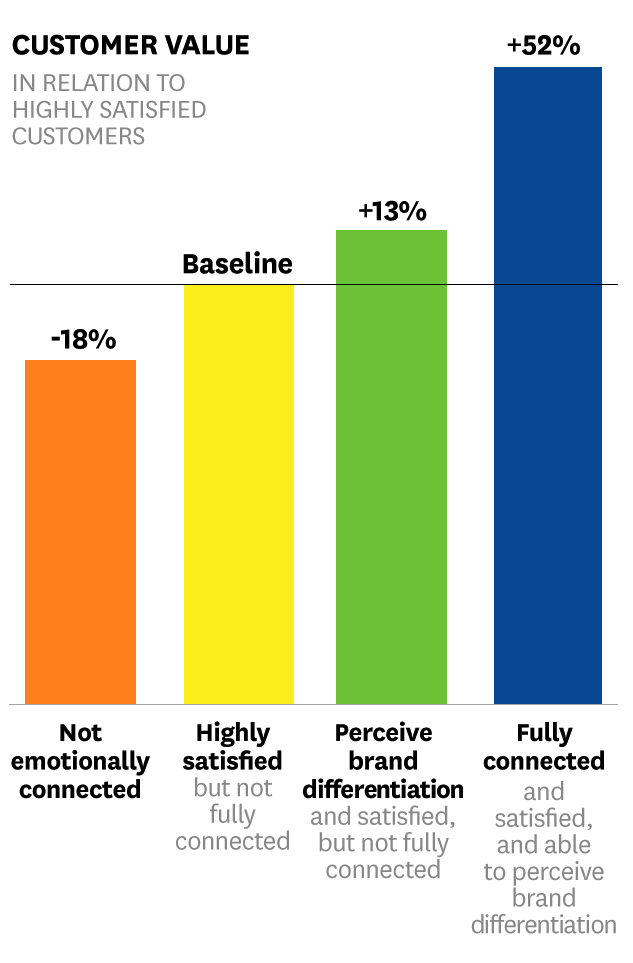
According to the Harvard Business Review, emotional connection to a brand is the key to long term business outcomes. Customers that have developed a bond with a business are in fact more valuable than highly satisfied customers; these customers, described as “fully connected” are actually 50% more valuable than the average customer. Therefore, if brands can win people over by forming emotional connections with them, brands can be highly influential in swaying customer perception.
How can brands form emotional bonds with customers if they do not understand them on an emotional level? By looking beyond customer survey data or online behavioral analytics, organizations can drive strong customer connections by speaking directly with them through brand market research, gaining valuable context on people’s motivations, current lifestyles and a range of other factors that shape their emotions, perceptions, and future decisions.
Why is customer perception important?
Perception does more than impact each individual purchase, it shapes the long-term relationships between customers and brands. This is often reflected in customer retention rates and the ability for brands to continue receiving relevant feedback and intelligence from their loyalists. Because of the importance of customer perception, every touchpoint between a company and its customers should strive to affect customer perception in a positive way.
Brands must also understand which elements have the broadest and most profound impact on customer perception. These elements can be both tangible and abstract, but each has the potential to be shaped by insights, CX, and UX professionals.
Some tangible factors that influence customers’ perceptions include:
- Price: Pricing a brand’s offerings should always be part of a comprehensive business strategy. However, it must be understood that context impacts customer perceived value (CPV) — lower prices are not always better, as any modern art dealer can ascertain.
- Quality: Quality can apply to multiple attributes in a product — attributes whose importance can differ from customer to customer. Marketers should understand what feature most distinguishes their products or services, and which are most desirable in target markets.
- Branding: Logos, artwork, and even packaging all deliver a message about a company and its brand. Marketers should ensure these elements meet and exceed customers’ expectations, helping brands stand above others.
- Service: Service quality will make or break customer perception, where even companies with superior products can lose business if customer support operations are not in place. Customers are more likely to write online reviews after highly positive or highly negative service experiences, which can improve or exacerbate brand awareness.
Some less-tangible factors that influence customers’ perceptions include:
- Advertising: How marketers deliver messages about a company, as well as the outlets they choose, can drive customers in both positive and negative directions.
- Reputation: Brand reputations are built over time and can be quite durable. They are formed from customer experiences with products and services, but also secondary interactions from third-parties (i.e. media coverage). While marketers attempt to measure their reputations online, sudden events can impact reputation without warning.
- Influencers: Influencers are people that customers trust, and are among the biggest factors impacting customer perception aside from the customer’s own personal experience. Customers that have firsthand experience with a product, service, or brand are most likely to sway other potential customers during the organizing stage.
What are the stages of customer perception?
To understand customer perception, researchers must first uncover insights into the customer experience (CX) and how it impacts customer perceived value (CPV). While many brand leaders understand the value of strong CX, customer experience quality continues to fall, having shrunk for 19% of brands in 2022 according to Forrester Research.
A number of factors can contribute to this downward CX trend — outdated ecommerce sites, labor shortages, etc. Whatever the reasons, it is apparent that many business leaders are growing more disconnected from their customers, and are failing to prioritize making people’s lives easier with their products and services. As a result, they are losing even more influence over customer perception.
CPV, or the importance ascribed to a brand’s offerings in terms of how much they are willing to spend on it, is equal to a customers’ perceived benefit minus its costs. Striking a balance between price and value is not an exact science, but it requires a large sample of context-based customer feedback using qualitative research methods to better understand.
Engaging with customers at scale not only brings organizations closer to understanding their customers, but it helps develop customer empathy across the business. With these objectives in mind, organizations can understand the phases of the customer perception process.
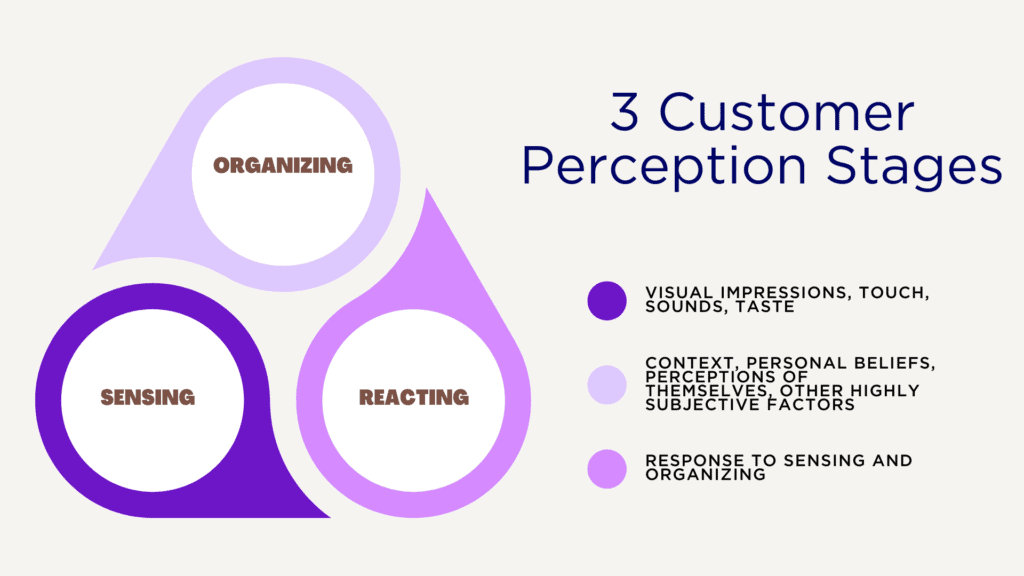
The three stages of customer perception include:
- Sensing: Characterized by the physical senses, customers use this stage to accumulate ‘knowledge’ about a product, service, or brand through physical sensations such as visual impressions, touch, sounds, and tastes.
- Organizing: During this stage, customers make sense of the information they’ve attained, interpreting its value based on context, personal beliefs, perceptions of themselves, and other highly subjective factors. At this stage, customers will categorize the object of their critique and compare it to other objects within their chosen categories. For example, a consumer hoping to buy a winter coat may prioritize coats by price, but also color and thickness, during the organizing stage.
- Reacting: Customers will act based upon the sensing and organizing stages; in addition, they are influenced by internal and external stimuli ranging from personal history to online reviews. Although each reaction and its contributing factors are different, buyers tend to experience similar processes of evaluation before making their decision.
Insights, CX and UX professionals who understand these three phases are better equipped to impact customer perceptions in a positive way. However, it’s impossible to capitalize on every contributing factor to shape customers’ behavior, as customers make tradeoffs, switching out one aspect of an offering for another of higher perceived value.
How to Understand Customer Perceptions
Understanding underlying motivations of consumer behavior through qualitative, brand market research is a strong method used by business leaders to influence customer perception and boost sales.
Brands have some ability to measure customer perception quantitatively, but this data is best understood and more profound when explaining it from customers themselves. Having conversations with customers helps to illuminate customer perceptions by probing and clarifying sentiment to uncover the heart of the ‘why’ behind their perceptions.
Discuss makes it easy for organizations to connect with customers and quickly turn their experiences into insights. Learn more about how to leverage qualitative research to improve CX with our infographic: “Using Customer Feedback for Customer Journey Pain Points.”