Artificial Intelligence (AI) has come a long way from gracing the pages of science fiction novels and movie screens featuring Arnold Schwarzenegger.
Instead of coming for our jobs (or our lives!) AI has stealthily integrated into the way we live, from auto-correcting that last text message you sent, to predicting the vessel performance of a transatlantic cargo fleet. Throughout the pandemic, the federal government has used AI to identify gaps in Covid-19 information, giving visibility to hospital data such as ventilator supplies and bed shortages.
Slowly but surely, the subset of AI known as machine learning is mitigating risks, predicting outcomes and future-proofing organizations.
And it’s impact has only begun. According to PwC, 45% of total economic gains by 2030 will come from AI-driven product enhancements, stimulating consumer demand. That is because AI and machine learning creates better product variety, increased personalization and affordability over time.
Unlike predictive analytics, which uses historical and existing data to identify patterns and behaviors to predict likely outcomes, machine learning builds its intelligence from algorithms that are not predetermined or rules-based, “learning” from past data without explicit programming.
Since machine learning processes and iterates large amounts of data quickly, it is an ideal vehicle for transforming the way that online qualitative feedback is analyzed for insight extraction. Put simply: it speeds the time to insights, and does it at scale.
Using AI for online qualitative research may not save lives, but it can get you closer to consumers by providing insights more quickly.
“AI is able to solve one of the biggest problems in the MRX industry, threading a needle through thousands of interviews and transforming disorganized raw data into powerful intelligence,” said Jim Longo, Discuss.io Co-Founder and Chief Operating Officer.
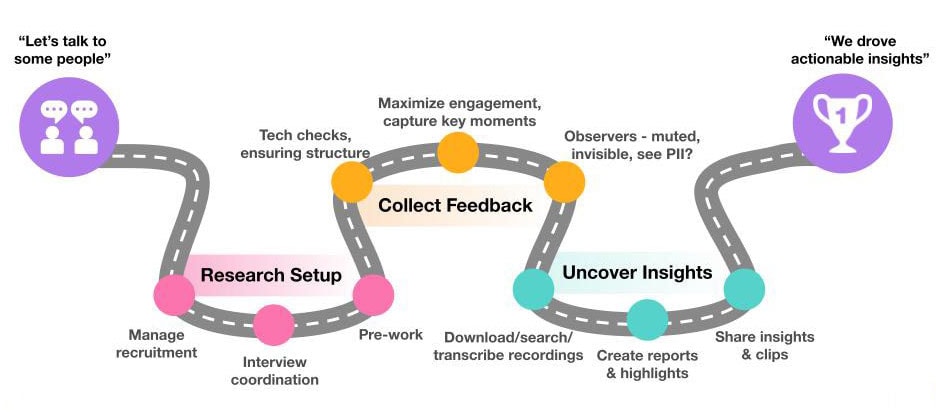
AI’s Role in Qualitative Research
Today, the availability of online qualitative research tools has created a major shift away from traditional market research through automation and streamlining workflows, cutting down on resources and administrative burden. Qualitative research need not rely on timely, costly and outdated processes.
With the introduction of AI and machine learning-powered research, the equation has further changed. Organizations can put the customer first even more by increasing productivity and making jobs simpler and more efficient.
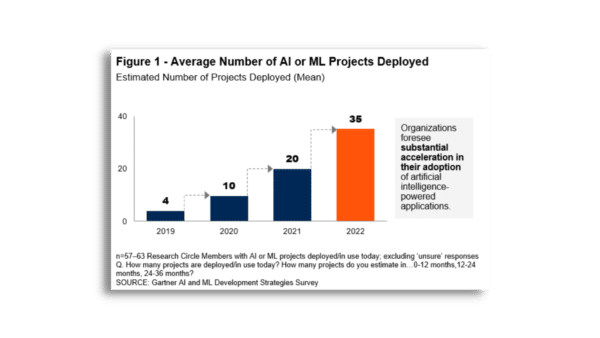
According to Gartner’s AI and ML Development Strategies Survey, 40% of organizations named CX as their top motivator to use AI technology. While technologies such as chat bots or virtual personal assistants can be used to serve external clients, most organizations (56%) use AI internally to support decision making and give recommendations to employees.
Jim Hare, research vice president at Gartner, said: “It is less about replacing human workers and more about augmenting and enabling them to make better decisions faster.”
Both discovering and sharing customer insights is now more seamless than ever, thanks to another subset of AI, Natural Language Processing (NLP). Gone are the days of endless transcriptions written manually during live focus groups or IDIs. NLP’s automatic translation function quickly analyzes vast amounts of language with accuracy and precision.
Platforms leveraging NLP such as Discuss.io are changing the game, with the ability to capture verbatims delivered instantly in multiple languages, which can then be processed quickly to find themes and patterns.
Another key benefit to using NLP for qualitative research is the ability to process people’s feelings and sentiments around key concepts and search terms. This function, called ‘sentiment analysis,’ scans textual data to determine whether that data is positive, negative, mixed or neutral. Researchers can then boil down people’s feedback to underlying emotions and associations with their organization’s brand or products.
These AI techniques enable organizations to reduce market research costs, decrease manual work by shrinking the timeline from asking questions to identifying learnings, and connect key data sources from multiple touch points.
In addition, machine learning can not only process qualitative data from current research projects, but it can mine past and historical data as well. This means that, if a researcher has not found an answer to an inquiry within current projects, they can search previous projects to find that veritable needle in a haystack.
This form of insights processing and searchability maximizes the insight potential of customer conversations, creating structure out of unstructured data.
Key Terms in AI-Driven Consumer Research
To review, here are the common terms used in practice:
- Machine learning: An AI technique or subset that leverages algorithms to analyze and draw inferences from data patterns, which enable it to learn and adapt without explicit programming.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Another subset of AI that refers to the automatic ability to process and understand human language with accuracy and precision.
- Sentiment analysis: The process of identifying and categorizing opinions expressed in a piece of text to determine an attitude toward a particular topic.
Discuss.io’s Augmented Insights
As Discuss.io further developed its people experience platform to better meet researchers’ needs, a suite of services emerged as a result of the ability to harness the power of AI. We refer to this suite of functionality as “Augmented Insights.”
Discuss.io’s Augmented Insights tools help teams move from interview to insights faster than ever with NLP, sentiment analysis and theme finding functions.
Learn how your team can leverage AI to drive qualitative analytics for better, faster, evidence-based decisions by viewing the infographic: “Using AI-powered Augmented Insights to Understand Consumers.”